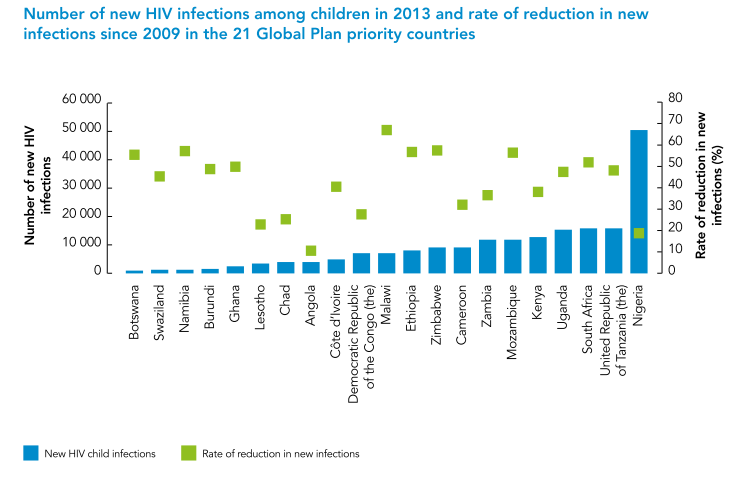
The 2014 UNAIDS Gap Report recognizes Malawi’s tremendous progress towards eliminating mother-to-child transmission of HIV. According to the latest epidemiological projections, Malawi achieved the largest reduction in infant infection rates in the world:
Infant HIV infection rates declined by 67% between 2009 and 2013
This achievment was based on a new policy for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission - developed and first implemeted in Malawi in 2011 - making life-long ART available for all HIV infected pregnant and breastfeeding women, regardless of clinical stage or CD4 count. This has resulted in a 66% reduction of vertical transmission within 3 years. This Malawi-pioneered strategy has since been included in global guidance by World Health organisation (WHO). As of February 2014, 12 other African countries were implementing Option B+.